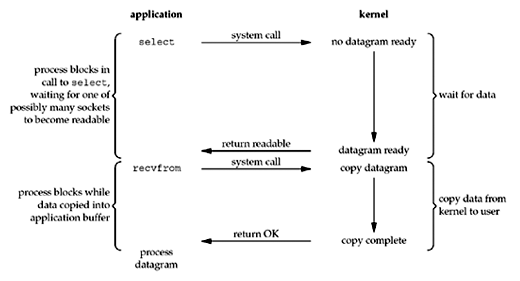
I/O Multiplexing Model
With I/O multiplexing, we call
select or poll and block in one of these two system calls, instead of blocking in the actual I/O system call. The figure is a summary of the I/O multiplexing model:
We block in a call to
select, waiting for the datagram socket to be readable. When select returns that the socket is readable, we then call recvfrom to copy the datagram into our application buffer.Comparing to the blocking I/O model *
Comparing Figure 6.3 to Figure 6.1:
- Disadvantage: using
selectrequires two system calls (selectandrecvfrom) instead of one - Advantage: we can wait for more than one descriptor to be ready (see the
selectfunction later in this chapter)
Multithreading with blocking I/O *
Another closely related I/O model is to use multithreading with blocking I/O. That model very closely resembles the model described above, except that instead of using
select to block on multiple file descriptors, the program uses multiple threads (one per file descriptor), and each thread is then free to call blocking system calls like recvfrom.